New to CBG and CBGa?
CBG and CBGa Explained

The History and Mystery of CBGa
CBGa is the acronym for cannabigerolic (can-nab-bi-ger-rol-lic) acid, which is a natural compound found in the Cannabis Sativa L. plant.
CBGa develops primarily in the trichomes of female cannabis hemp and marijuana plants. The trichomes are the microscopic-sized, mushroom-like structures on the plant's flowers that produce cannabinoids. When these plants are in the flowering stage, the initial cannabinoid compound created is CBGa.
Confusion, Research & Evolution
For decades, CBG was mistakenly called the 'Mother of all cannabinoids' because CBGa had never been researched in depth. But in 1999, Japanese cannabis researchers proved that CBGa—not CBG—is the original source of all cannabis cannabinoids.
Another world-renowned cannabis researcher and organic chemist, Dr. Raphael Mechoulam (called the 'Father of cannabis science'), confirmed that CBGa is the precursor.
Dr. Mechoulam is best known for isolating THC, CBD, CBG, and several other cannabinoids 60 years ago (1963-1973), and he never stopped researching. He also initiated cooperation between cannabis scientific research teams worldwide (including the USA). Mechoulam and his selected groups of scientists spent decades studying the chemistry, pharmacology, and clinical effects of natural products (including cannabis). They made thousands of fascinating breakthrough discoveries about how cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) potentially affect various medical conditions.
The ECS works directly with CBGa to help your body achieve balance (homeostasis). It regulates your body's biochemistry and physiology—including learning and memory, mood, sleep, appetite, metabolism, immune responses, reproduction, growth, and development.
Are CBG & CBGa The Same?
If you have been researching CBD products, you may have encountered two similar (but newer) acronyms: CBG and CBGa. While these two cannabinoid acronyms were previously used interchangeably, CBG and CBGa have very different properties.
What is CBGa?
CBGa stands for cannabigerolic acid, which is most notable for creating all other 100+ cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. Still, initial research shows it has its therapeutic qualities because CBGa primarily works with the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) in the brain and Central Nervous System. Recent ECS studies suggest that CBGa protects our brains from oxidative stress, helps with enhanced memory, alertness, and focus, and makes our bodies more receptive to other cannabinoids.
What is CBG?
CBG stands for cannabigerol, and it is non-acidic. When exposed to heat, CBGa's carboxyl acids convert into CBG. ECS research suggests that CBG's main benefits come from its ability to improve moods, reduce inflammation, and help relieve sore muscles and joints. Maybe that's why CBG is a popular ingredient added to many CBD-based products today.
CBG and CBGa are both non-addictive, non-intoxicating, and federally legal (less than 0.3% THC) cannabinoids derived from hemp, but each State has specific laws regarding cannabis and hemp.
While successful CBG human clinical trials have been done in other countries, CBG and CBGa are now gaining attention from US researchers and scientists working on medicinal chemistry and pharmacology studies.
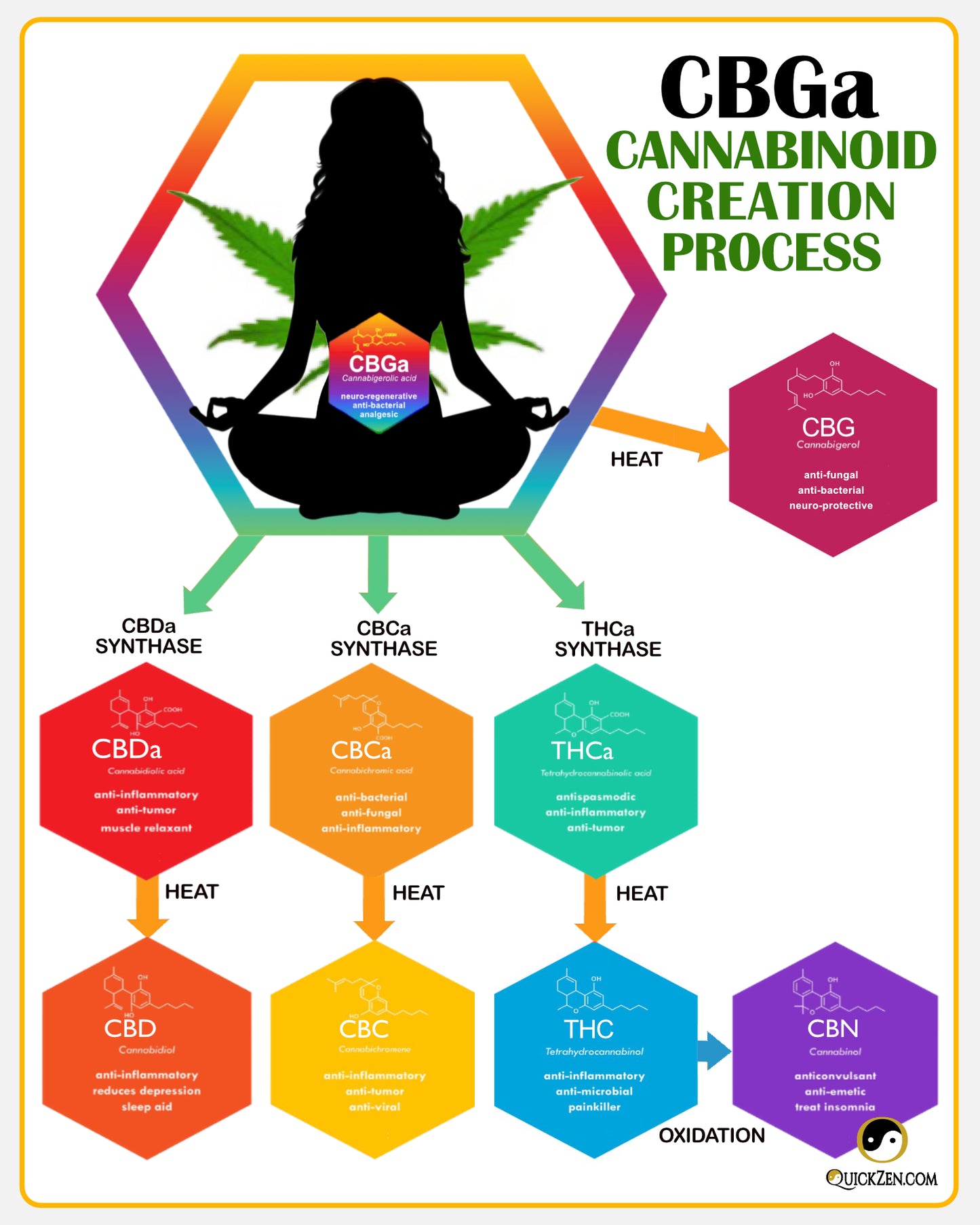
How CBGa Creates All Other Cannabinoids
It all starts with CBGa (Cannabigerolic acid), the first compound produced from the Sativa L. plant. CBGa is essential because it is the 'stem cell' of 100+ cannabinoids (can-nab-in-noids), including CBG, THC, CBD, and all others. In fact, without CBGa, no other cannabis (hemp or marijuana) compounds would even exist.
CBGa simply converts into CBG when exposed to UV light or heat. CBGa also breaks down into all other cannabinoids through a natural but more complex internal process called enzymatic synthase that changes the plants' biochemistry.
How does CBGa make cannabinoid compounds?
- CBG is the only organic cannabinoid that doesn't undergo a synthase process to become active. It's one step away from CBGa. In our bodies, CBG imitates endocannabinoids (en-doe-can-nab-bi-noids)—the natural, internal cannabis-like compounds our body actually makes.
- CBGa also converts into other acid compounds after the plant goes through synthase. It breaks down into THCa, CBDa, and CBCa (the 'a' stands for an acid group, organic and natural acids (like amino acids).
- When decarboxylated with heat, these acid compounds transform again into the more well-known, neutral cannabinoids called THC, CBD, and CBC. It's a two-step process to make them.
- Creating CBN requires a three-step process because it comes directly from THC. The plant must first go through the synthase process to break down into THCa, next it is decarbed to change into neutral THC, and then it converts into CBN after an aging or oxidation process.
And this is the way Mother Nature works.

What's The Difference Between CBD and CBG?
CBD is the acronym for cannabidiol (can-nab-ih-dye-all), and CBG stands for cannabigerol (can-nab-bi-ger-rol). These two cannabinoids are both found in cannabis and hemp plants, but they are often confused due to their similarities.
CBD and CBG offer numerous potential benefits, but they differ in their molecular structure and how they interact with your body's internal Endocannabinoid System (ECS).
How do CBD & CBG work?
- CBD - Best for Nighttime: Helps you unwind, creates a sense of relaxation, and helps with stress and anxiety. (Works with the ECS primarily on your body!)
- CBG - Best for Daytime: Gives you a sense of calm and general well-being, with better focus and concentration. (Works with the ECS primarily on your brain and central nervous system!)
While the two of them potentially benefit our overall wellness in various ways, they each offer unique properties that make them attractive options for natural topical applications for multiple issues, such as muscle stress and inflammation.
Both CBD and CBG are non-addictive, non-psychotropic, and anti-inflammatory cannabinoids. So you can experience all their benefits without worrying about annoying side effects! But everyone's body reacts differently to each of these compounds.
Be Research Aware: There's a lot of old and obsolete information online about CBG and CBGa! If you want to learn more about cannabis, we suggest you start with a YouTube.com search for Dr. Raphael Mechoulam (the 'Father of cannabis science'). It's a fascinating 60+ year journey in cannabis research!



